Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
The entropy of a probability density function (PDF) 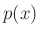 is
defined as
is
defined as
where lg
denotes the logarithm base 2. The entropy of 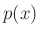 can
be interpreted as the average number of bits needed to specify random
variables
can
be interpreted as the average number of bits needed to specify random
variables 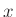 drawn at random according to
drawn at random according to 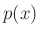 :
:
The term
lg![$ [1/p(x)]$](img110.png) can be viewed the number of bits which should
be assigned to the value
can be viewed the number of bits which should
be assigned to the value 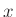 . (The most common values of
. (The most common values of 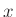 should
be assigned the fewest bits, while rare values can be assigned many
bits.)
should
be assigned the fewest bits, while rare values can be assigned many
bits.)
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[Comment on this page via email]
![]() is
defined as
is
defined as
![$\displaystyle \zbox{h(p) \isdef \int_x p(x) \cdot \mbox{lg}\left[\frac{1}{p(x)}\right] dx}
$](img108.png)
![$\displaystyle h(p) = {\cal E}_p\left\{\mbox{lg}\left[\frac{1}{p(x)}\right]\right\}
$](img109.png)