 Computational models of music styles
Computational models of music styles
 Modeling music as Markov chains - composer identification
Modeling music as Markov chains - composer identification
 Motivation
Motivation
To describe how music is modeled by Markov chains, let's first define
the terminologies and notations -
A first order, discrete time Markov chain
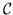 is a random walk
is a random walk
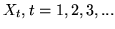 ,
in a state space
,
in a state space
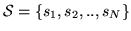 according to a
according to a
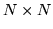 state-transition matrix
state-transition matrix
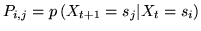 ,
where
,
where  denotes the element on the
denotes the element on the
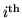 row and
row and
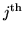 column,
and
column,
and
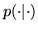 is the usual notation of the
conditional probability distribution function.
is the usual notation of the
conditional probability distribution function.
Mathematically, it suffices to say that a Markov chain
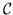 is
characterized by its state-transition matrix
is
characterized by its state-transition matrix 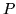 , up to
one-to-one mappings between homeomorphic state spaces. One can even
sloppily write
, up to
one-to-one mappings between homeomorphic state spaces. One can even
sloppily write
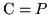 .
However, how the transition
matrix actually means depends upon how the state-space is defined.
For example, if the (pentatonic) state space is defined as
.
However, how the transition
matrix actually means depends upon how the state-space is defined.
For example, if the (pentatonic) state space is defined as
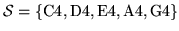 , then
, then
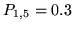 reads ``the next note is G4 thirty percents of the times when the
current note is C4.''
reads ``the next note is G4 thirty percents of the times when the
current note is C4.''
Since higher-order Markov chains are beyond the scope of this research, in
the rest of this paper, ``Markov chains'' means first-order ones
unless otherwise mentioned.
Subsections
 Computational models of music styles
Computational models of music styles
 Modeling music as Markov chains - composer identification
Modeling music as Markov chains - composer identification
 Motivation
Motivation
Copyright © 2002-06-11
Center for Computer Research in Music and Acoustics,
Stanford University
![]() is
characterized by its state-transition matrix
is
characterized by its state-transition matrix ![]() , up to
one-to-one mappings between homeomorphic state spaces. One can even
sloppily write
, up to
one-to-one mappings between homeomorphic state spaces. One can even
sloppily write
![]() .
However, how the transition
matrix actually means depends upon how the state-space is defined.
For example, if the (pentatonic) state space is defined as
.
However, how the transition
matrix actually means depends upon how the state-space is defined.
For example, if the (pentatonic) state space is defined as
![]() , then
, then
![]() reads ``the next note is G4 thirty percents of the times when the
current note is C4.''
reads ``the next note is G4 thirty percents of the times when the
current note is C4.''