Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Now we may isolate the filter phase response
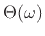 by
taking a ratio of the
by
taking a ratio of the  and
and  in Eq.(1.5):
in Eq.(1.5):
Substituting the expansions of  and
and  yields
yields
Thus, the phase response of the simple lowpass filter
 is
is
 |
(2.7) |
We have completely solved for the frequency response of the simplest
low-pass filter given in Eq.(1.1) using only trigonometric
identities. We found that an input sinusoid of the form
produces the output
Thus, the gain versus frequency is
 and the change in
phase at each frequency is given by
and the change in
phase at each frequency is given by  radians. These functions
are shown in Fig.1.7. With these functions at our disposal,
we can predict the filter output for any sinusoidal input. Since, by
Fourier theory [84], every signal can be represented as a sum
of sinusoids, we've also solved the more general problem of predicting the
output given any input signal.
radians. These functions
are shown in Fig.1.7. With these functions at our disposal,
we can predict the filter output for any sinusoidal input. Since, by
Fourier theory [84], every signal can be represented as a sum
of sinusoids, we've also solved the more general problem of predicting the
output given any input signal.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() by
taking a ratio of the
by
taking a ratio of the ![]() and
and ![]() in Eq.(1.5):
in Eq.(1.5):
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\frac{b(\omega)}{a(\omega)}
&=& -\frac{G(\omega) \sin\left[\Theta(\omega)\right]}{G(\omega) \cos\left[\Theta(\omega)\right]}\\
&=& -\frac{\sin\left[\Theta(\omega)\right]}{\cos\left[\Theta(\omega)\right]}\\
&\isdef & - \tan[\Theta(\omega)]
\end{eqnarray*}](img169.png)
![]() and
and ![]() yields
yields
![\begin{eqnarray*}
\tan[\Theta(\omega)] &=& - \frac{b(\omega)}{a(\omega)} \\
&=& - \frac{\sin(\omega T)}{1 + \cos(\omega T)}\\
&=& - \frac{2\sin(\omega T/2)\cos(\omega T/2)}{1 + [\cos^2(\omega T/2) - \sin^2(\omega T/2)]}\\
&=& - \frac{2\sin(\omega T/2)\cos(\omega T/2)}{2\cos^2(\omega T/2)}
= - \frac{\sin(\omega T/2)}{\cos(\omega T/2)}
= \tan\left(-\omega T/2\right).
\end{eqnarray*}](img170.png)
![]() is
is