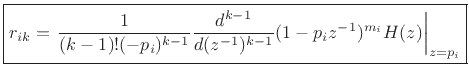Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Dealing with Repeated Poles Analytically
A pole of multiplicity 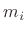 has
has
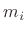 coefficients7.9 associated with it. For example,
coefficients7.9 associated with it. For example,
and the three coefficients associated with the pole 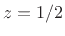 are 1, 2, and 4.
are 1, 2, and 4.
Let 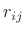 denote the
denote the 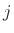 th coefficient associated with the pole
th coefficient associated with the pole 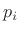 ,
,
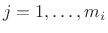 .
Successively differentiating
.
Successively differentiating
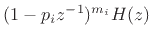
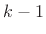 times with
respect to
times with
respect to 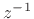 and setting
and setting 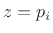 isolates the coefficient
isolates the coefficient 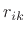 :
:
or
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() has
has
![]() coefficients7.9 associated with it. For example,
coefficients7.9 associated with it. For example,
![]() denote the
denote the ![]() th coefficient associated with the pole
th coefficient associated with the pole ![]() ,
,
![]() .
Successively differentiating
.
Successively differentiating
![]()
![]() times with
respect to
times with
respect to ![]() and setting
and setting ![]() isolates the coefficient
isolates the coefficient ![]() :
:
![\begin{eqnarray*}
r_{i1} &=& \left.(1-p_iz^{-1})^{m_i}H(z)\right\vert _{z=p_i}\\ [5pt]
r_{i2} &=& \left.\frac{1}{-p_i}\frac{d}{dz^{-1}} (1-p_iz^{-1})^{m_i}H(z)\right\vert _{z=p_i}\\ [5pt]
r_{i3} &=& \left.\frac{1}{2(-p_i)^2}\frac{d^2}{d(z^{-1})^2} (1-p_iz^{-1})^{m_i}H(z)\right\vert _{z=p_i}\\ [5pt]
r_{i4} &=& \left.\frac{1}{3\cdot 2(-p_i)^3}\frac{d^3}{d(z^{-1})^3} (1-p_iz^{-1})^{m_i}H(z)\right\vert _{z=p_i}
\end{eqnarray*}](img765.png)