Research

Personalized HRTF Modeling using DNN-Augmented BEM
Accurate modeling of personalized head-related transfer functions (HRTFs) is difficult but critical for applications requiring spatial audio. However, this remains challenging as experimental measurements require specialized equipment, numerical simulations require accurate head geometries and robust solvers, and data-driven methods are hungry for data. In this paper, we propose a new deep learning method that combines measurements and numerical simulations to take the best of three worlds. By learning the residual difference and establishing a high quality spatial basis, our method achieves consistently 2 dB to 2.5 dB lower spectral distortion (SD) compared to the state-of-the-art methods.
Web
PDF
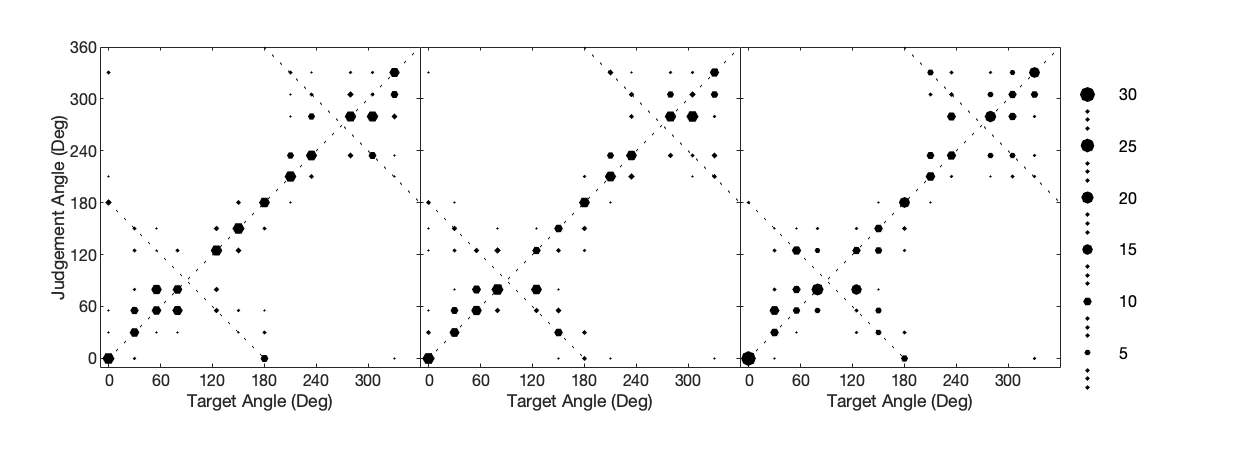
Individual Distance-Dependent HRTFs Modeling through a Few Anthropometric Measurements
The lack of data is a major problem in individual HRTF modeling. There are many HRTF databases, but each database only has limited HRTFs and has its own characteristics, such as distance-dependent HRTFs or individual HRTFs. How to effectively model HRTFs through several different databases is an important task. In this paper, a method for predicting individual distance-dependent HRTFs using a few anthropometric parameters is proposed. By modeling the HRTFs in CIPIC database, which contains individual HRTFs in 1 meter, and the PKU&IOA database, which contains KEMAR HRTFs in eight distances, we predict the individual HRTFs in arbitrary directions and distances. The objective experiments show that the proposed model has less spectral distortions than distance variation function model. The subjective experiments show that the proposed model can predict the individual HRTFs in arbitrary directions and distances.
PDF
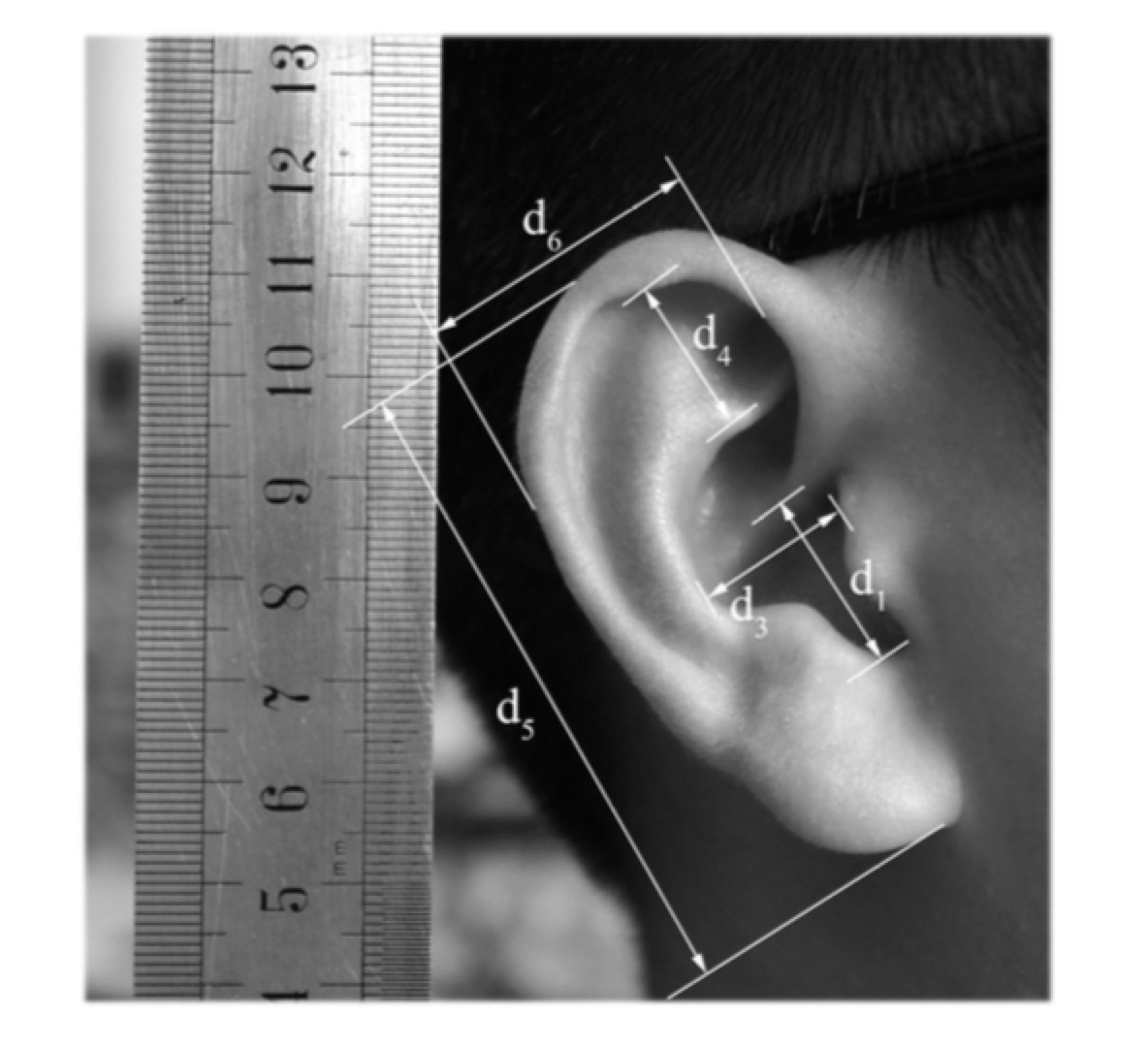
Modeling of Individual HRTFs based on Spatial Principal Component Analysis
Head-related transfer function (HRTF) plays an important role in the construction of 3D auditory display. This paper presents an individual HRTF modeling method using deep neural networks based on spatial principal component analysis. The HRTFs are represented by a small set of spatial principal components combined with frequency and individual-dependent weights. By estimating the spatial principal components using deep neural networks and mapping the corresponding weights to a quantity of anthropometric parameters, we predict individual HRTFs in arbitrary spatial directions. The objective and subjective experiments evaluate the HRTFs generated by the proposed method. The objective experiments' results show that the HRTFs generated by the proposed method perform better than the generic method and similar to the PCA method. Meanwhile, eighteen subjects participated in the subjective experiments, and the results indicate that the localization performance of the proposed method is desired in both the azimuth localization and the elevation localization.
PDF

Distance-Dependent Modeling of Head-Related Transfer Functions
A method for modeling distance dependent HRTFs is presented. The HRTFs are first decomposed by spatial principal component analysis (SPCA). Using deep neural networks (DNN), we model the spatial principal component weights of different distances. Then we realize the prediction of HRTFs in arbitrary spatial distances. The objective and subjective experiments are conducted to evaluate the proposed distance model and the distance variation function model, and the results have shown that the proposed model has less spectral distortions than distance variation function model, and the virtual sound generated by the proposed model has better performance in terms of distance localization.
PDF

Individualized HRTF-based Binaural Renderer for Higher-Order Ambisonics
Ambisonics is a promising spatial sound technique in augmented and virtual reality. In our previous study, we modeled the individual head-related transfer functions (HRTFs) using deep neural networks based on spatial principal component analysis. This paper proposes an individualized HRTF-based binaural renderer for the higher-order Ambisonics. The binaural renderer is implemented by filtering the virtual loudspeaker signals using individualized HRTFs. We perform subjective experiments to evaluate generic and individualized binaural renderers. Results show that the individualized binaural renderer has front-back confusion rates that are significantly lower than those of the generic binaural renderer. Therefore, we validate that using individualized HRTFs to convolve with those virtual loudspeaker signals to generate virtual sound at an arbitrary spatial direction still performs better than those using generic HRTFs. In addition, by measuring or modeling individual’s HRTFs in a small set of directions, our proposed binaural renderer system effectively predict individual’s HRTFs in arbitrary spatial directions.
PDF

An Asynchronous HRTF Measurement Method based on Phase Alignment
In HRTF measurement, the Maximum Length Sequence (MLS), the sweep signal, and impulse signal are usually used as the exciting signal and played in loop to generate several HRTFs and then the HRTFs are averaged to improve the Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR) of the results. However, the inconsistency of the timing modules (Oscillator) used in the recording system and in the playback system results the time non-alignment between the measured HRTFs in different played loop. The time non-alignment destroys the function of the average process and makes the average results distortion. For solving this problem, an asynchronous HRTF measurement method based on the phase alignment is proposed. The evaluation experiment results show that the Peak-SNR of the proposed HRTF measured method are improved about 4.5 dB compare to that of the traditional method.
PDF

Comparison and Realization of the HRTF Measurements
A series of comparison and analysis on measured methods for different exciting signal are carried out. Based on surveying variety kinds of measuring method for HRTF, four kinds of commonly used methods: MLS method, Golay code method, frequency sweep signal in the frequency domain method and time domain method are used. Respectively, we did the measurement for HRTF in the anechoic chamber and meeting room based on the four methods, horizontal angle ranged from 0 to 360 at 30 degrees’ step. Meanwhile, based on the measured HRTFs, the verified experiments were carried on these four methods. After that, the experiments were done to analyze the advantages and disadvantages of these four methods. The experimental results show that the frequency sweep signal in the time domain method performed better than the other three methods in noise immunity and
nonlinear systems.






