Glossary
- Continuous Controller (CC)
- A type of MIDI message typically used for the expressive,
realtime, control of synthesis parameters. The origin of these messages
lies in the need to transmit over MIDI, information from controllers
such as modulation wheel and pitch bender. Continuous Controller
messages are a generalization of this idea, and are not necessarily
associated with any particular type of controlling device.
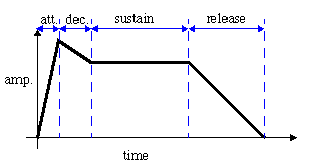
- Envelope Generator (EG)
- A synthesizer module, typically (although not necessarily) used
for shaping amplitude with respect to time. Envelope Generators
typically allow input signal to be shaped into four different segments:
attack, decay, sustain, and release. These are illustrated in Figure
13.
Figure 13: A Typical Envelope Generator (EG)
- Digitally Controlled Oscillator (DCO)
- The digital counterpart of the Voltage Controlled Oscillator
(VCO), commonly found on digital synthesizers. Unlike the VCO, the
waveform produced is in the form of a sequence of numbers (hence
digital) which are later converted to an electrical signal using a
Digital to Analog Converter (DAC).
- Frequency Modulation (FM)
- A synthesis method brought into popular usage with the Yamaha
DX7, a synthesizer which took advantage of technology developed at
CCRMA by John Chowning. Essentially, Frequency Modulation is a form
of vibrato which is so fast that pitch modulations become smeared
into the audio spectrum, resulting in additional partials, known as
sidebands.
- Low Frequency Oscillator (LFO)
- An oscillator used for modulating synthesis parameters at the
note and/or phrase level. On the Oberhiem OB-Mx, for example, the
LFOs offer a choice of 4 possible waveforms, and can be assigned to
practically any synthesis parameter. Their speeds can be adjusted
within the range: 0.1 to 30.0 Hz.
- Low Pass Filter (LPF)
- A filter which attenuates high frequency content of an input
signal, while allowing low frequency components to pass through
unimpeded. A High Pass Filter (HPF) does the opposite.
- MIDI
- Acronym standing for Musical Instrument
Digital Interface.
MIDI is the standard protocol used by electronic instrument
manufacturers to enable one device to communicate with another.
- Radio Baton
- A device developed by Max Mathews for controlling electronic
musical instruments via MIDI. The position in 3-dimensional space of
(up to) 2 batons are tracked with the aid of radio technology housed
in a separate processing unit.
- Voltage Controlled Filter (VCF)
- A module commonly found on analog synthesizers, which alters the
spectral content of its input - for example, increasing the
brightness of a tone. Usual control parameters include: frequency
(or cut-off frequency), which adjusts the center-point of the
filter; and resonance, which adjusts the width of the filter.
- Voltage Controlled Oscillator (VCO)
- A module commonly found on analog synthesizers, producing
periodic waveforms in the form of a continuously varying electrical
signal, which are used as the basis of sound synthesis. Typically,
these waveforms have rich spectral content, and before final output,
are filtered (further modifying the spectral content), and enveloped
(shaping the amplitude of the waveform with respect to time).
Notes on the CD
The accompanying CD10
features a recording of Cosmos made on the
occasion of its premiere at the CCRMA Summer concert, which took place
on July 24, 1997, at the Knoll courtyard on the Stanford University
campus.

