Property.
re![]() for
for
![]() whenever
whenever
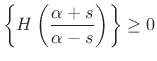
for re
Proof.
We shall show that the change of variable
![]() ,
provides a conformal map from the z-plane to the s-plane that takes the
region
,
provides a conformal map from the z-plane to the s-plane that takes the
region
![]() to the region
re
to the region
re![]() . The general formula for a
bilinear conformal mapping of functions of a complex variable is given by
. The general formula for a
bilinear conformal mapping of functions of a complex variable is given by
In general, a bilinear transformation maps circles and lines into circles
and lines [83]. We see that the choice of three specific points
and their images determines the mapping for all ![]() and
and ![]() .
We must have that the imaginary axis in the s-plane maps to the unit circle
in the z-plane.
That is, we may determine the mapping by three points of the form
.
We must have that the imaginary axis in the s-plane maps to the unit circle
in the z-plane.
That is, we may determine the mapping by three points of the form
![]() and
and
![]() .
If we predispose one such mapping by choosing the pairs
.
If we predispose one such mapping by choosing the pairs
![]() and
and
![]() , then we are left with
transformations of the form
, then we are left with
transformations of the form
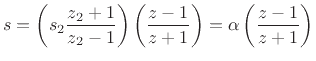
or

which gives us that
There is a bonus associated with the restriction that ![]() be real which
is that
be real which
is that
We have therefore proven
Property.
 PR
PRwhere
The class of mappings of the form Eq.(C.85) which take the exterior of the unit circle to the right-half plane is larger than the class Eq.(C.86). For example, we may precede the transformation Eq.(C.86) by any conformal map which takes the unit disk to the unit disk, and these mappings have the algebraic form of a first-order complex allpass whose zero lies inside the unit circle.
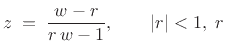 real
realwhich maps the real axis to the real axis. This leads only to the composite transformation,
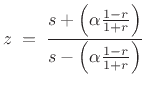
which is of the form Eq.(C.86) up to a minus sign (rotation by
The bilinear transform is one which is used to map analog filters into
digital filters. Another such mapping is called the matched ![]() transform [365]. It also preserves the positive real
property.
transform [365]. It also preserves the positive real
property.
Property. ![]() is PR if
is PR if ![]() is positive real in the analog
sense, where
is positive real in the analog
sense, where ![]() is interpreted as the sampling period.
is interpreted as the sampling period.
Proof. The mapping
![]() takes the right-half
takes the right-half ![]() -plane to
the outer disk in the
-plane to
the outer disk in the ![]() -plane. Also
-plane. Also ![]() is real if
is real if ![]() is
real. Hence
is
real. Hence ![]() PR implies
PR implies ![]() PR. (Note, however, that
rational functions do not in general map to rational
functions.)
PR. (Note, however, that
rational functions do not in general map to rational
functions.)![]()
These transformations allow application of the large battery of tests which exist for functions positive real in the right-half plane [528].