Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Rewriting the filter in state-space form,2we have
or
where
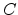
![$ ^T=[c_1,c_2]=[0, 1]$](img79.png) and
and 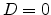 . As is well known, the transfer
function of a state-space model (A,B,C,D) is given by
. As is well known, the transfer
function of a state-space model (A,B,C,D) is given by
where
Thus, under all choices of input or output, there is at most one real
finite zero at
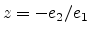 .
.
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Download smac03maxjos.pdf
![$\displaystyle \left[\begin{array}{c} x(n+1) \\ [2pt] y(n+1) \end{array}\right]
...
...ray}\right]
+
\left[\begin{array}{c} b_1 \\ [2pt] b_2 \end{array}\right] u(n)
$](img69.png)
![$\displaystyle \left[\begin{array}{c} x(n+1) \\ [2pt] y(n+1) \end{array}\right]
...
...ray}\right]
+
\left[\begin{array}{c} b_1 \\ [2pt] b_2 \end{array}\right] u(n)
$](img69.png)