Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Let
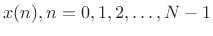 , denote an
, denote an 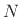 -sample complex sequence,
i.e.,
-sample complex sequence,
i.e.,
 . Then the spectrum of
. Then the spectrum of 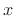 is defined by the
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT):
is defined by the
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT):
The inverse DFT (IDFT) is defined by
In this chapter, we will omit mention of an explicit sampling interval
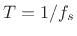 , as this is most typical in the digital signal processing
literature. It is often said that the sampling frequency is
, as this is most typical in the digital signal processing
literature. It is often said that the sampling frequency is 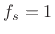 .
In this case, a radian frequency
.
In this case, a radian frequency
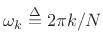 is in
units of ``radians per sample.'' Elsewhere in this book,
is in
units of ``radians per sample.'' Elsewhere in this book, 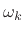 usually means ``radians per second.'' (Of course, there's no
difference when the sampling rate is really
usually means ``radians per second.'' (Of course, there's no
difference when the sampling rate is really 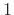 .) Another term we use
in connection with the
.) Another term we use
in connection with the 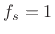 convention is normalized
frequency: All normalized radian frequencies lie in the range
convention is normalized
frequency: All normalized radian frequencies lie in the range
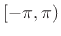 , and all normalized frequencies in Hz lie in the range
, and all normalized frequencies in Hz lie in the range
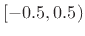 .7.1 Note that physical units
of seconds and Hertz can be reintroduced by the substitution
.7.1 Note that physical units
of seconds and Hertz can be reintroduced by the substitution
Subsections
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
Index |
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
[How to cite this work] [Order a printed hardcopy] [Comment on this page via email]
![]() , denote an
, denote an ![]() -sample complex sequence,
i.e.,
-sample complex sequence,
i.e.,
![]() . Then the spectrum of
. Then the spectrum of ![]() is defined by the
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT):
is defined by the
Discrete Fourier Transform (DFT):


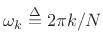 is in
units of ``radians per sample.'' Elsewhere in this book,
is in
units of ``radians per sample.'' Elsewhere in this book,