Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
To digitize via the bilinear transform, we make the substitution
where 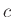 is any positive real constant (typically
is any positive real constant (typically 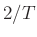 ).
).
For the ideal mass reflectance
the bilinear transform yields
with
Note that 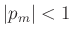 and
and
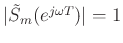 . The stable allpass
nature of the digitized mass reflectance is preserved by the bilinear
transform, as always.
. The stable allpass
nature of the digitized mass reflectance is preserved by the bilinear
transform, as always.
Important Observation:
If we choose 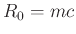 , then
, then 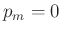 and
and
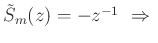 no delay-free path through the mass reflectance
no delay-free path through the mass reflectance
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Download WaveDigitalFilters.pdf
Download WaveDigitalFilters_2up.pdf
Download WaveDigitalFilters_4up.pdf
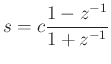
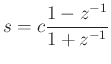
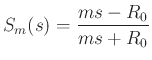
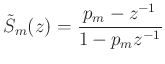
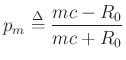
![]() , then
, then ![]() and
and
![]() no delay-free path through the mass reflectance
no delay-free path through the mass reflectance