We started by collecting articles about pitch detection to see what other people had done. Based on this research, we held a short oral report about the pros and cons of the various time-domain, frequency-domain, and combined techniques. The maximum likelihood seemed like a good decision as
- it was supposed to function well for musical signals,
- it wasn't as complicated as other methods that used neural networks for example,
- and we even had a chance to test out the fiddle~ object in Max/MSP, which implements a similar algorithm in real-time.
So, we went ahead and started writing the program to perform pitch detection with MATLAB. Mostly taking turns, one of us would work hard on the code for a week, while the other would give advice. As we couldn't find many good samples on the internet, we recorded some of our own.
The program-flow in the final version was:
- select an audio file in the GUI and display the contents
- wait for the input parameters and the command to start the analysis
- segment the audio file into windows
- perform the following for each window:
- the window is zero-padded to increase resolution in frequency domain
- the FFT is taken
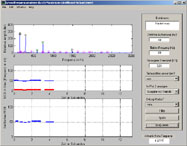
- the result of the FFT is optionally filtered and then displayed (see picture below)
- the peaks in the frequency domain are selected by looking for changes in the derivative
- magenta circles are drawn around the peaks
- the highest peaks are chosen
- green circles are drawn around these highest peaks
- the likelihood that each of the green circles represents the pitch is calculated given the other peaks
- the green circle with the highest likelihood is then chosen as the pitch for the frame
- a black box is drawn around it
- if the variance between this and the previous results is low enough, then this pitch is accepted as valid and plotted in the bottom graph
To Download: