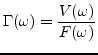 |
(3) |
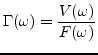 |
(3) |
where for a given frequency ![]() , the ratio between
the Fourier Transform of the velocity and force is known.
A physical explanation of the driving-point
admittance is to view the admittance
as a measure of how readily force
exerted at the contact point at a certain frequency results in
motion at that same frequency [23].
Since the body of the guitar
is a rigid structure that exhibits standing waves at particular
frequencies, known as the modes of the guitar, the body
vibrates naturally at these frequencies.
Notable modes include the air mode and the first few
body modes.
, the ratio between
the Fourier Transform of the velocity and force is known.
A physical explanation of the driving-point
admittance is to view the admittance
as a measure of how readily force
exerted at the contact point at a certain frequency results in
motion at that same frequency [23].
Since the body of the guitar
is a rigid structure that exhibits standing waves at particular
frequencies, known as the modes of the guitar, the body
vibrates naturally at these frequencies.
Notable modes include the air mode and the first few
body modes.
A brief overview of the mechanics of our physical model thus far: the string vibrates upon excitation. Its end is connected to the body of the instrument at the bridge, exerting energy from the initial pluck at the fundamental frequency and its harmonic series. According to the driving-point admittance, the force applied at the bridge by the string results in motion of the bridge and top-plate. The resulting motion is dependent upon the construction of the top-plate of the instrument which determines its modes of vibration. The acoustic instrument then propagates pressure waves according to its top-plate movement, thereby coloring the resulting pressure waves heard by our ears.