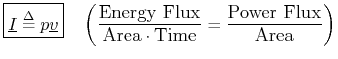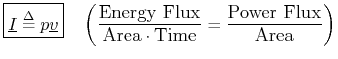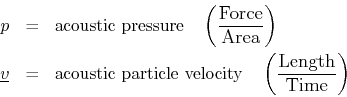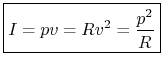Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
REALSIMPLE Top
Acoustic Intensity may be defined by
where
For a plane traveling wave, we have
where
is called the wave impedance of air, and
Therefore, in a plane wave,
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
REALSIMPLE Top
Download Delay.pdf
Download Delay_2up.pdf
Download Delay_4up.pdf