Difference between revisions of "Incorporate"
m (Research documentation for Incorporate by Chris Lortie) |
m (Research documentation for Incorporate by Chris Lortie) |
||
| (18 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This wiki page serves as a multimedia research documentation for the piece ''Incorporate'' by Chris Lortie and attempts to analyze its compositional rhetoric. ''Incorporate'' was written in early 2018 (premiered March 10, 2018) for a subset of [ | + | This wiki page serves as a multimedia research documentation for the piece ''Incorporate'' by Chris Lortie and attempts to analyze its compositional rhetoric. ''Incorporate'' was written in early 2018 (premiered March 10, 2018) for a subset of [https://ensembleproton.ch/en/ Ensemble Proton] consisting of flute, clarinet, violin, and cello. The piece makes use of very minimal electronics that are entirely fixed and non-interactive. Although the premiere of ''Incorporate'' made use of a fifth performer (designated as the “Operator”) as well as theatrical staging and costuming, these elements will not be reviewed here. The piece is largely improvisatory and makes use of audio score(s) as the primary means of composer-performer communication. A supplementary written PDF is provided as a verbal reiteration of contents from the audio score(s). |
| − | + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/incorporate-unmastered.wav A full recording of the work can be cound here (recorded 11 March, 2018 at Elliot Program Center, Stanford University -- Ensemble Proton)] | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | [[File:Frontview.PNG|500px|thumb|right|front view of ensemble at the premiere]] | |
| − | == | + | ==Audio Scores and Affordances== |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The piece was inspired by my research with Charlie Sdraulig into the various affordances and limitations of the audio score format. An audio score can be defined as a score which employs sound as the primary means of communication between composer and performer. As opposed to conventionally-noted written scores, audio scores represent information and instructions within the same domain as the performed product (Sdraulig and Lortie, 2018). | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Many of the arguments in that paper, and some of the arguments in this documentation, are posited within the context of affordance theory. Affordances can be defined as “the potential actions made possible by an object or environment to a given individual,” a concept that implies a mutually-influencing, transactional relation between actor and object (Gibson, 1979. p. 172). A material format alone does not wholly determine the action possibilities it affords; composers and performers (i.e. the actors in this context), as well as audio scores (i.e. the object), are themselves situated and dynamically shaped within wider networks and histories of cultural practice. These practices mediate and constrain potential relations: for instance, the act of deploying a sound recording as if it were a score suggests a translation of prior scoring practices across media; equally, functioning as a score is just one of the many potential use cases afforded by sound recordings. Nevertheless, at this particular intersection of cultural practice and material format, audio scores representing information and instructions in sound afford some distinct and different possibilities to composers and performers when compared to scores which deploy some form of symbolic visual representation of sound or sound-producing movement. ''Incorporate'' was conceived as an applied study of these affordances, along with an exploration of possible new applications for this medium. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | ''' | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''case studies referenced in Charlie Sdraulig and Chris Lortie, ''An Investigation of Affordances and Limitations in Recent Audio Scores'', 2018'''<nowiki> |
| − | + | - Cassandra Miller — Guide | |
| − | + | - Carola Bauckholt — Zugvögel | |
| − | + | - Louis d’Heudieres — Laughter Studies 1-3 | |
| − | + | - Carolyn Chen — Adagio | |
| − | + | - Laura Stanic — Open Air Bach</nowiki> | |
| − | == | + | The Sdraulig/Lortie paper surveyed a collection of recent audio scores primarily associated with experimental art music as case studies. Among these, we identified two primary sub-categories associated with the temporal relations composed between performer and audio score: reactive and rehearsed. On the one hand, performers primarily react to the audio score during performance; on the other, the audio score shapes the performers’ interpretations in rehearsal, well before public performance. In practice, these two categories may be combined, weighted, and hybridized to varying degrees. After this research, I became interested in this hybridized deployment of the audio score object and sought to create a piece which features several layers — or modes — of audio scores simultaneously. |
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==The Four Modes of Audio Score in ''Incorporate''== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Incorporate'' makes use of four distinct modes of audio scores which serve to communicate instruction in different areas of the composition. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Mode 1: Instructions=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Category: Rehearsed | ||
| + | - Format: Fixed Audio Files (7) and Video Overview | ||
| + | - Contents: Narration, Instructions, Exercises | ||
| + | |||
| + | The first mode of audio score deployed in this piece comes in the form of the score’s instructive narration. This narration is segmented into eight files, including one video overview, and seven audio files. The video overview provides an explanation of the structure, development, and actions performed within the piece. The seven audio files serve to demonstrate and clarify the musical events of the piece along with their boundaries and internal logic. | ||
| + | |||
| + | This narration could be likened to an “audiobook” version of a conventional text score, with the exception that this score takes advantage of the unique affordances of recorded audio. Here, the audio format serves not only to instruct but actively engage the listener through a series of musical exercises. These exercises invite participation in real time from the performer and serve as a tool for individual rehearsal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | For example, one exercise consists of a 15-minute meditation with a particular focus towards deep listening and sound reproduction. Another consists of alternating narrated and interactive segments which serve to progressively build up in complexity. The primary affordance enacted by this mode of the audio score is in demonstrating a specific system of listening and interaction. Furthermore, the score arguably benefits from representing these instructions in the same domain as the performed product, affording an immediacy of communication. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The use of an audio score as a means to direct modes of listening can also be observed in Hildegard Westerkamp’s [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=hg96nU6ltLk ''Kits Beach Soundwalk'']. The piece, existing as a static audio file, provides narrated commentary of a soundwalk at Kits Beach in Vancouver: | ||
| + | |||
| + | "[...] I'm trying to listen to those tiny sounds in more detail now. Suddenly, the background sound of the city seems louder again. It interferes with my listening. It occupies all acoustic space and I can't hear the barnacles in all their tininess. It seems too much effort to filter the city out. Luckily, we have bandpass filters and equalizers. We can just go into the studio and get rid of the city -- pretend it's not there. Pretend we are somewhere far away..." (Westerkamp, 1989) | ||
| + | |||
| + | Like other members of the [https://www.sfu.ca/sonic-studio/WSP/index.html World Soundscape Project] (M. Schaefer, Truax, et al.), Westerkamp is keen on pointing out the complex layering of our contemporary soundscapes; unlike her colleagues, however, she makes an effort to espouse these modern distractions by pondering their unique complexity. Likewise, she promotes the technological tools available to effectuate this goal, referencing “bandpass filters and equalizers.” By making public her own listening practice, Westerkamp invites the listener to empathize and engage with these narrated observations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Mode 2: Sound Files=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Category: Rehearsed | ||
| + | - Format: Fixed Audio Files (60) | ||
| + | - Contents: Concrete Sounds, Field Recordings, Sampled Material | ||
| + | |||
| + | The second mode of audio score used in ''Incorporate'' takes the form of sound files that are provided before every rehearsal and performance. Each performer is given three recordings, ranging from 5 seconds to 30 seconds in length. The performers were not given descriptions of what was contained within each file, but were instead instructed (via mode 1’s narration) to focus only on sonic qualities. During the piece, the players are instructed to perform a faithful reproduction these sound files on their particular instrument in the form of an ongoing loop; this material serves as the initial starting point for the ensemble’s improvisations for each formal section. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/SF-narration.wav Excerpt from Mode 1's Narration explaining the use of Sound Files in Mode 2] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The sound files are comprised of a collection of field recordings and sampled materials, and are assigned to a player based upon an assumed affinity to their instrument. These allocations were done as an attempt to reduce the amount of translation between recording and performer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The sound files and their contents were selected to be consistent across certain criterea towards specific ends. For instance: | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''·''' Most soundfiles are non-pitched, or do not contain easily-discernable pitch. This affords a homogenous texture to the ensemble that is weighted towards non-pitched sounds and extended techniques. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''·''' Most soundfiles are shorter than 10 seconds long. This affords a detailed scrutiny of their rhythmic and timbral qualities, as anything longer than 10 seconds would not be easily compressed into the player’s echoic memory. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''·''' Most soundfiles do not have large variations in dynamic over time, and generally do not contain abrupt jumps in dynamic. This affords a slowly-evolving ensemble dynamic that benefits more from textural information than dramatic or gestural information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''·''' All recordings have been reduced to mono, which prevents the performer from being distracted or influenced by spatial information. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Some examples of sound files used in Incorporate: | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/SF-1.wav Example 1] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/SF-2.wav Example 2] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/SF-3.wav Example 3] | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/SF-4.wav Example 4] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The last example on this list was used on the day of the premiere performance. In the excerpt below, one can hear the clarinet player Richard Haynes reproducing this sound on his instrument from memory. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/mode-2-excerpt.wav Excerpt with Clarinet reproduction of Example 4 above] | ||
| + | |||
| + | This mode of the audio score was directly influenced by a similar implementation in ''Zugvögel'' by Carola Bauckholt. ''Zugvögel'' is a reed quintet in which players interact with and rehearse the audio score well before public performance. The audio recordings, which consist of bird calls of various species, are not played in performance; instead, the quintet members are instructed to familiarize themselves with these bird calls and memorize all their time-based nuances in order to reproduce them on their respective instruments. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/Bauckholt_AB.wav Excerpt of birdsong recording and subsequent reproduction of recording on instruments] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Bauckholt’s use of the audio score format directs this activity towards high-fidelity transcriptions of bird calls rather than reduced abstraction or overt musicalization (the obvious historical precedent for the latter occurs in the works of Olivier Messiaen) (O'Callaghan, 2012). By using recordings of her sources, Bauckholt’s audio score affords of a higher degree of specificity and dimensionality to performers than most visual, symbolic representation of those sources (particularly in regards to spectro-temporal variation in timbre, for example.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Zugvogel.PNG|400px|thumb|left|visual score for ''Zugvögel'']] | ||
| + | |||
| + | In ''Zugvögel'', each performer establishes a distinct relationship with the recordings due to their objective of producing a faithful imitation through whatever means necessary. This mimetic process begins with the task of parsing each recording’s most salient elements. In contrast to the traditional practice of bird call transcription in a conventionally-notated medium, the recorded format omits much of the symbolic filtering and prioritizations of the composer. It instead defers any such filtering to the instrumentalists of the reed quintet, allowing a more intimate understanding of the instruments’ capabilities to inform a precise rendering. Hence, the performers’ personal knowledge of their instrument’s compatibility with the source material affords a higher degree of fidelity in its reproduction. Through this process, the performer may also come to discover previously hidden action-potentials in relation to their instrument. | ||
| + | |||
| + | It should be noted that each recording is symbolically transcribed by Bauckholt in an accompanying visual score. She adds in her prefatory notes, however, that “the notation should only be taken as a guide,” suggesting that the notated transcription holds only a supplementary role in relation to the audio score (Bauckholt, 2011-12). However, this visual aid helps to mitigate one of the audio score format’s primary limitations: the act of memorization. Because the minute features of each recording must be encoded into memory and recalled in performance, the musical information itself is subject to variability and even corruption over time. Factors influencing the performer’s ability to reproduce the recording may include: the time spent rehearsing, the effort expended in memorizing the recording, the recognizability (or lack thereof) of each sound, the player’s aptitude or preferences towards certain sounds, and/or the player’s assumed ensemble role during performance. Employing a visual score in conjunction with the audio score would seem to effectively redress this limitation. | ||
| + | |||
| + | By contrast, the sound files provided in ''Incorporate'' are purposefully not supplemented with an accompanying visual score. The score’s contents are thus subject to a lower-fidelity translation via the performer’s memorized impression. ''Incorporate'' instead opts for a qualitative embodiment of the audio score, relying on the mediations of the performers’ identities and subjective inclinations to shape the source material. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Mode 3: Shocks=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Category: Reactive | ||
| + | - Format: Fixed Audio Files (15) with randomized timings | ||
| + | - Contents: Sampled Material | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Incorporate-form.png|350px|thumb|right|formal diagram of Incorporate]] | ||
| + | |||
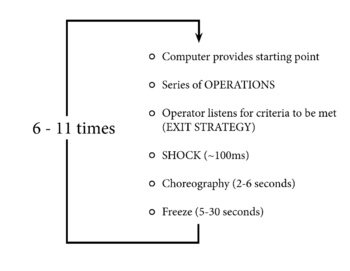
| + | The third mode of the audio score comes in the form of the electronics during performance. The electronics consist of very short sound files (each less than a second long) played at a high volume, each triggered at random intervals over the course of the piece. These serve the role of enforcing the pacing and form of the piece as a whole by demarcating the beginning of each formal section. The form of ''Incorporate'' resembles simple loop of actions that happens anywhere from 6 to 11 times. The electronic “shocks” serve to signal the beginning of a new loop. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Here, the audio score falls into the reactive category, because the players are asked to respond to these shocks in real time. They cannot anticipate the shocks and have no forewarning that they are about to occur. The use of both unpredictability and indeterminacy affords the performance a certain level of theatrical anxiety. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Below is an example of one of these shocks in the context of the performance. In this excerpt, players react to the shock in real time by performing a specific action (the anxious breathing). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~cjl93/incorporate-wiki/mode-3-excerpt.wav Excerpt with a shock] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The use of a reactive audio score as a means to create anxiety can also be seen in Becky Brown’s ''Tomorrow, When I Grow Up''. Brown’s piece, scored for solo voice and electronics, varies between each performance. Although the electronics are entirely fixed, they are rearranged in a DAW between rehearsals and performances by the composer so that they cannot be feasibly predicted. This affords the soloist a certain amount of performance anxiety in the subsequent performance, aligning with the programmatic narrative of the work (Brown, 2018). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://becky-brown.org/work/tomorrow-when-i-grow-up link to Becky Brown's ''Tomorrow, When I Grow Up''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | === Mode 4: Operations === | ||
| + | |||
| + | - Category: Reactive | ||
| + | - Format: Live Performance | ||
| + | - Contents: Improvised material from ensemble | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Panels.PNG|450px|thumb|left|computer screen display showing operations]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The fourth mode of the audio score comes in the form of 19 operations, or keywords, that serve as improvisatory cues. These are displayed on a computer screen in real time by an operator, who stands behind the ensemble at a laptop. The operations are designated as an audio score because the players perform real-time manipulations of each other’s improvised material. The verbal cues given on the screen do not dictate what sounds are to be produced, but instead direct the players towards what to attend to as source material and how to manipulate that material. Conceivably any sound can be filtered through these operations. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Players come to be familiarized with each of these operations through the aforementioned audio narration of Mode 1. The operations are defined and clarified through exercises and meditations. These set the expectations and boundaries for possible use cases in performance. The vocabulary of operations is modular, in that the list of possible keywords can be amended or reduced for a given performance. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Incorporate-stage-setup-small.PNG|450px|thumb|left|stage diagram for Incorporate]] | ||
| − | |||
:{| class="wikitable" | :{| class="wikitable" | ||
|+ | |+ | ||
| − | ! | + | !Name of Operation |
| − | ! | + | !Description (simplified) |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Incorporate |
| − | |'' | + | |''incorporate the sonic environment into current material'' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Articulate |
| − | |'' | + | |''make the beginning of each musical event more distinguishable'' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Embellish |
| − | |'' | + | |''determine the most salient features of the texture and add accentuating information'' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Clarify |
| − | |'' | + | |''make different types of sounds within the texture more distinct from each other'' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | | + | |Specialize |
| − | |'' | + | |''observe affordances of instrument and merge material with those unique possibilities'' |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Constrain | |
| − | + | |''observe the restrictions of the instrument and force the musical material against those limitations'' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Mediate | |
| − | + | |''produce the current sound through different physical means'' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | |Trail | ||
| + | |''act as a delay line for another instrument'' | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Granulate | |
| − | + | |''continuously rearrange the previous material; reorder musical segments in new ways'' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| + | |Consolidate | ||
| + | |''remove the silences between events'' | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Suspend | |
| − | + | |''sounds should be continuous, with no perceptible re-entry'' | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Pause | |
| + | |''pause activity with a memory of the current material loop'' | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | |Resume | ||
| + | |''resume activity as if nothing during the pause has transpired'' | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Interrupt | |
| + | |''rearrange your current material as interruptions to another player’s activity take attention away from this player'' | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| + | |Evade | ||
| + | |''avoid playing at the same time as any other player'' | ||
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |Support | |
| + | |''emphasize and align with material in one other player’s improvisations; support them'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Provide | ||
| + | |''establish what is needed in the environment and provide that resource'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Hide | ||
| + | |''execute all events with the aim of drawing attention away from oneself'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |} | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| − | + | Bauckholt, Carola. ''Zugvögel'' for reed quintet. Freiburg, Germany: Thuermchen Verlag, 2011-12. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Brown, Becky, “Tomorrow, When I Grow Up,” Composer's personal website, Published February 26, 2018 http://becky-brown.org/work/tomorrow-when-i-grow-up. | |
| − | + | ||
| + | Gibson, James Jerome. ''The Ecological Approach to Visual Perception''. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 1979. | ||
| + | |||
| + | O'Callaghan, James. "Mediated Mimesis: Transcription as Processing." In Ems-network.org. ''Proceedings of the Electroacoustic Music | ||
| + | Studies Network Conference: Meaning and Meaningfulness in Electroacoustic Music''. Stockholm., 2012. http://www.ems-network.org/IMG/pdf_EMS12_ocallaghan.pdf. | ||
| − | + | Score Follower. "Carola Bauckholt — Zugvögel [w/ score]." YouTube video, 12:39, December 1, 2013. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KEAHxLNyVxw. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Sdraulig, Charlie and Chris Lortie, ''An Investigation of Affordances and Limitations in Recent Audio Scores'', 2018 | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | Westerkamp, Hildegard, ''Kits Beach Soundwalk,'' 1989. | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
Latest revision as of 00:39, 15 June 2018
This wiki page serves as a multimedia research documentation for the piece Incorporate by Chris Lortie and attempts to analyze its compositional rhetoric. Incorporate was written in early 2018 (premiered March 10, 2018) for a subset of Ensemble Proton consisting of flute, clarinet, violin, and cello. The piece makes use of very minimal electronics that are entirely fixed and non-interactive. Although the premiere of Incorporate made use of a fifth performer (designated as the “Operator”) as well as theatrical staging and costuming, these elements will not be reviewed here. The piece is largely improvisatory and makes use of audio score(s) as the primary means of composer-performer communication. A supplementary written PDF is provided as a verbal reiteration of contents from the audio score(s).
Contents
Audio Scores and Affordances
The piece was inspired by my research with Charlie Sdraulig into the various affordances and limitations of the audio score format. An audio score can be defined as a score which employs sound as the primary means of communication between composer and performer. As opposed to conventionally-noted written scores, audio scores represent information and instructions within the same domain as the performed product (Sdraulig and Lortie, 2018).
Many of the arguments in that paper, and some of the arguments in this documentation, are posited within the context of affordance theory. Affordances can be defined as “the potential actions made possible by an object or environment to a given individual,” a concept that implies a mutually-influencing, transactional relation between actor and object (Gibson, 1979. p. 172). A material format alone does not wholly determine the action possibilities it affords; composers and performers (i.e. the actors in this context), as well as audio scores (i.e. the object), are themselves situated and dynamically shaped within wider networks and histories of cultural practice. These practices mediate and constrain potential relations: for instance, the act of deploying a sound recording as if it were a score suggests a translation of prior scoring practices across media; equally, functioning as a score is just one of the many potential use cases afforded by sound recordings. Nevertheless, at this particular intersection of cultural practice and material format, audio scores representing information and instructions in sound afford some distinct and different possibilities to composers and performers when compared to scores which deploy some form of symbolic visual representation of sound or sound-producing movement. Incorporate was conceived as an applied study of these affordances, along with an exploration of possible new applications for this medium.
case studies referenced in Charlie Sdraulig and Chris Lortie, An Investigation of Affordances and Limitations in Recent Audio Scores, 2018 - Cassandra Miller — Guide - Carola Bauckholt — Zugvögel - Louis d’Heudieres — Laughter Studies 1-3 - Carolyn Chen — Adagio - Laura Stanic — Open Air Bach
The Sdraulig/Lortie paper surveyed a collection of recent audio scores primarily associated with experimental art music as case studies. Among these, we identified two primary sub-categories associated with the temporal relations composed between performer and audio score: reactive and rehearsed. On the one hand, performers primarily react to the audio score during performance; on the other, the audio score shapes the performers’ interpretations in rehearsal, well before public performance. In practice, these two categories may be combined, weighted, and hybridized to varying degrees. After this research, I became interested in this hybridized deployment of the audio score object and sought to create a piece which features several layers — or modes — of audio scores simultaneously.
The Four Modes of Audio Score in Incorporate
Incorporate makes use of four distinct modes of audio scores which serve to communicate instruction in different areas of the composition.
Mode 1: Instructions
- Category: Rehearsed - Format: Fixed Audio Files (7) and Video Overview - Contents: Narration, Instructions, Exercises
The first mode of audio score deployed in this piece comes in the form of the score’s instructive narration. This narration is segmented into eight files, including one video overview, and seven audio files. The video overview provides an explanation of the structure, development, and actions performed within the piece. The seven audio files serve to demonstrate and clarify the musical events of the piece along with their boundaries and internal logic.
This narration could be likened to an “audiobook” version of a conventional text score, with the exception that this score takes advantage of the unique affordances of recorded audio. Here, the audio format serves not only to instruct but actively engage the listener through a series of musical exercises. These exercises invite participation in real time from the performer and serve as a tool for individual rehearsal.
For example, one exercise consists of a 15-minute meditation with a particular focus towards deep listening and sound reproduction. Another consists of alternating narrated and interactive segments which serve to progressively build up in complexity. The primary affordance enacted by this mode of the audio score is in demonstrating a specific system of listening and interaction. Furthermore, the score arguably benefits from representing these instructions in the same domain as the performed product, affording an immediacy of communication.
The use of an audio score as a means to direct modes of listening can also be observed in Hildegard Westerkamp’s Kits Beach Soundwalk. The piece, existing as a static audio file, provides narrated commentary of a soundwalk at Kits Beach in Vancouver:
"[...] I'm trying to listen to those tiny sounds in more detail now. Suddenly, the background sound of the city seems louder again. It interferes with my listening. It occupies all acoustic space and I can't hear the barnacles in all their tininess. It seems too much effort to filter the city out. Luckily, we have bandpass filters and equalizers. We can just go into the studio and get rid of the city -- pretend it's not there. Pretend we are somewhere far away..." (Westerkamp, 1989)
Like other members of the World Soundscape Project (M. Schaefer, Truax, et al.), Westerkamp is keen on pointing out the complex layering of our contemporary soundscapes; unlike her colleagues, however, she makes an effort to espouse these modern distractions by pondering their unique complexity. Likewise, she promotes the technological tools available to effectuate this goal, referencing “bandpass filters and equalizers.” By making public her own listening practice, Westerkamp invites the listener to empathize and engage with these narrated observations.
Mode 2: Sound Files
- Category: Rehearsed - Format: Fixed Audio Files (60) - Contents: Concrete Sounds, Field Recordings, Sampled Material
The second mode of audio score used in Incorporate takes the form of sound files that are provided before every rehearsal and performance. Each performer is given three recordings, ranging from 5 seconds to 30 seconds in length. The performers were not given descriptions of what was contained within each file, but were instead instructed (via mode 1’s narration) to focus only on sonic qualities. During the piece, the players are instructed to perform a faithful reproduction these sound files on their particular instrument in the form of an ongoing loop; this material serves as the initial starting point for the ensemble’s improvisations for each formal section.
Excerpt from Mode 1's Narration explaining the use of Sound Files in Mode 2
The sound files are comprised of a collection of field recordings and sampled materials, and are assigned to a player based upon an assumed affinity to their instrument. These allocations were done as an attempt to reduce the amount of translation between recording and performer.
The sound files and their contents were selected to be consistent across certain criterea towards specific ends. For instance:
· Most soundfiles are non-pitched, or do not contain easily-discernable pitch. This affords a homogenous texture to the ensemble that is weighted towards non-pitched sounds and extended techniques.
· Most soundfiles are shorter than 10 seconds long. This affords a detailed scrutiny of their rhythmic and timbral qualities, as anything longer than 10 seconds would not be easily compressed into the player’s echoic memory.
· Most soundfiles do not have large variations in dynamic over time, and generally do not contain abrupt jumps in dynamic. This affords a slowly-evolving ensemble dynamic that benefits more from textural information than dramatic or gestural information.
· All recordings have been reduced to mono, which prevents the performer from being distracted or influenced by spatial information.
Some examples of sound files used in Incorporate:
The last example on this list was used on the day of the premiere performance. In the excerpt below, one can hear the clarinet player Richard Haynes reproducing this sound on his instrument from memory.
Excerpt with Clarinet reproduction of Example 4 above
This mode of the audio score was directly influenced by a similar implementation in Zugvögel by Carola Bauckholt. Zugvögel is a reed quintet in which players interact with and rehearse the audio score well before public performance. The audio recordings, which consist of bird calls of various species, are not played in performance; instead, the quintet members are instructed to familiarize themselves with these bird calls and memorize all their time-based nuances in order to reproduce them on their respective instruments.
Excerpt of birdsong recording and subsequent reproduction of recording on instruments
Bauckholt’s use of the audio score format directs this activity towards high-fidelity transcriptions of bird calls rather than reduced abstraction or overt musicalization (the obvious historical precedent for the latter occurs in the works of Olivier Messiaen) (O'Callaghan, 2012). By using recordings of her sources, Bauckholt’s audio score affords of a higher degree of specificity and dimensionality to performers than most visual, symbolic representation of those sources (particularly in regards to spectro-temporal variation in timbre, for example.)
In Zugvögel, each performer establishes a distinct relationship with the recordings due to their objective of producing a faithful imitation through whatever means necessary. This mimetic process begins with the task of parsing each recording’s most salient elements. In contrast to the traditional practice of bird call transcription in a conventionally-notated medium, the recorded format omits much of the symbolic filtering and prioritizations of the composer. It instead defers any such filtering to the instrumentalists of the reed quintet, allowing a more intimate understanding of the instruments’ capabilities to inform a precise rendering. Hence, the performers’ personal knowledge of their instrument’s compatibility with the source material affords a higher degree of fidelity in its reproduction. Through this process, the performer may also come to discover previously hidden action-potentials in relation to their instrument.
It should be noted that each recording is symbolically transcribed by Bauckholt in an accompanying visual score. She adds in her prefatory notes, however, that “the notation should only be taken as a guide,” suggesting that the notated transcription holds only a supplementary role in relation to the audio score (Bauckholt, 2011-12). However, this visual aid helps to mitigate one of the audio score format’s primary limitations: the act of memorization. Because the minute features of each recording must be encoded into memory and recalled in performance, the musical information itself is subject to variability and even corruption over time. Factors influencing the performer’s ability to reproduce the recording may include: the time spent rehearsing, the effort expended in memorizing the recording, the recognizability (or lack thereof) of each sound, the player’s aptitude or preferences towards certain sounds, and/or the player’s assumed ensemble role during performance. Employing a visual score in conjunction with the audio score would seem to effectively redress this limitation.
By contrast, the sound files provided in Incorporate are purposefully not supplemented with an accompanying visual score. The score’s contents are thus subject to a lower-fidelity translation via the performer’s memorized impression. Incorporate instead opts for a qualitative embodiment of the audio score, relying on the mediations of the performers’ identities and subjective inclinations to shape the source material.
Mode 3: Shocks
- Category: Reactive - Format: Fixed Audio Files (15) with randomized timings - Contents: Sampled Material
The third mode of the audio score comes in the form of the electronics during performance. The electronics consist of very short sound files (each less than a second long) played at a high volume, each triggered at random intervals over the course of the piece. These serve the role of enforcing the pacing and form of the piece as a whole by demarcating the beginning of each formal section. The form of Incorporate resembles simple loop of actions that happens anywhere from 6 to 11 times. The electronic “shocks” serve to signal the beginning of a new loop.
Here, the audio score falls into the reactive category, because the players are asked to respond to these shocks in real time. They cannot anticipate the shocks and have no forewarning that they are about to occur. The use of both unpredictability and indeterminacy affords the performance a certain level of theatrical anxiety.
Below is an example of one of these shocks in the context of the performance. In this excerpt, players react to the shock in real time by performing a specific action (the anxious breathing).
The use of a reactive audio score as a means to create anxiety can also be seen in Becky Brown’s Tomorrow, When I Grow Up. Brown’s piece, scored for solo voice and electronics, varies between each performance. Although the electronics are entirely fixed, they are rearranged in a DAW between rehearsals and performances by the composer so that they cannot be feasibly predicted. This affords the soloist a certain amount of performance anxiety in the subsequent performance, aligning with the programmatic narrative of the work (Brown, 2018).
link to Becky Brown's Tomorrow, When I Grow Up
Mode 4: Operations
- Category: Reactive - Format: Live Performance - Contents: Improvised material from ensemble
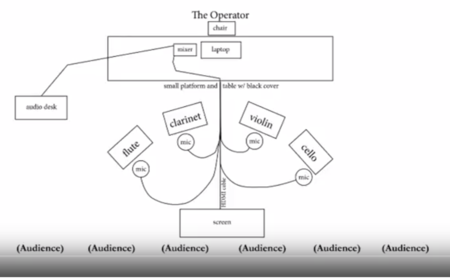
The fourth mode of the audio score comes in the form of 19 operations, or keywords, that serve as improvisatory cues. These are displayed on a computer screen in real time by an operator, who stands behind the ensemble at a laptop. The operations are designated as an audio score because the players perform real-time manipulations of each other’s improvised material. The verbal cues given on the screen do not dictate what sounds are to be produced, but instead direct the players towards what to attend to as source material and how to manipulate that material. Conceivably any sound can be filtered through these operations.
Players come to be familiarized with each of these operations through the aforementioned audio narration of Mode 1. The operations are defined and clarified through exercises and meditations. These set the expectations and boundaries for possible use cases in performance. The vocabulary of operations is modular, in that the list of possible keywords can be amended or reduced for a given performance.
Name of Operation Description (simplified) Incorporate incorporate the sonic environment into current material Articulate make the beginning of each musical event more distinguishable Embellish determine the most salient features of the texture and add accentuating information Clarify make different types of sounds within the texture more distinct from each other Specialize observe affordances of instrument and merge material with those unique possibilities Constrain observe the restrictions of the instrument and force the musical material against those limitations Mediate produce the current sound through different physical means Trail act as a delay line for another instrument Granulate continuously rearrange the previous material; reorder musical segments in new ways Consolidate remove the silences between events Suspend sounds should be continuous, with no perceptible re-entry Pause pause activity with a memory of the current material loop Resume resume activity as if nothing during the pause has transpired Interrupt rearrange your current material as interruptions to another player’s activity take attention away from this player Evade avoid playing at the same time as any other player Support emphasize and align with material in one other player’s improvisations; support them Provide establish what is needed in the environment and provide that resource Hide execute all events with the aim of drawing attention away from oneself
References
Bauckholt, Carola. Zugvögel for reed quintet. Freiburg, Germany: Thuermchen Verlag, 2011-12.
Brown, Becky, “Tomorrow, When I Grow Up,” Composer's personal website, Published February 26, 2018 http://becky-brown.org/work/tomorrow-when-i-grow-up.
Gibson, James Jerome. The Ecological Approach to Visual Perception. Boston: Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, 1979.
O'Callaghan, James. "Mediated Mimesis: Transcription as Processing." In Ems-network.org. Proceedings of the Electroacoustic Music Studies Network Conference: Meaning and Meaningfulness in Electroacoustic Music. Stockholm., 2012. http://www.ems-network.org/IMG/pdf_EMS12_ocallaghan.pdf.
Score Follower. "Carola Bauckholt — Zugvögel [w/ score]." YouTube video, 12:39, December 1, 2013. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=KEAHxLNyVxw.
Sdraulig, Charlie and Chris Lortie, An Investigation of Affordances and Limitations in Recent Audio Scores, 2018
Westerkamp, Hildegard, Kits Beach Soundwalk, 1989.