Difference between revisions of "Stompbox Faust Effects"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | This tutorial is provided as part of the 2016 CCRMA Stompbox workshop and was written by Romain Michon. | + | This tutorial is provided as part of the [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/wiki/Stompbox_2016 2016 CCRMA Stompbox workshop] and was written by Romain Michon. |
[http://faust.grame.fr Faust] is a functional programming language for real time signal processing. It allows to easily make a wide range of objects going from VST plug-ins to iOS apps for different platforms. This quick tutorial shows how to generate advanced audio effects for PureData using Faust. | [http://faust.grame.fr Faust] is a functional programming language for real time signal processing. It allows to easily make a wide range of objects going from VST plug-ins to iOS apps for different platforms. This quick tutorial shows how to generate advanced audio effects for PureData using Faust. | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
[[Image:stompbox_faust2pd.png|900px|center]] | [[Image:stompbox_faust2pd.png|900px|center]] | ||
| − | "~/faust/demo/cryBaby.pd" | + | "~/faust/demo/cryBaby.pd" demonstrates how to use a Faust generated PD external. The first inlet takes messages that can be used to control the different parameters of the object. All the other inlets are audio inputs. Similarly, the first outlet can be used to retrieve messages and other outlets are audio outputs. To get a list of the parameters of the object, a bang can be sent to the first inlet and the list will be sent to the first outlet. For example, when a bang is sent to "cryBaby~" (from cryBaby.dsp), the following list is returned: |
print: checkbox /CRYBABY/Bypass 0 0 0 1 1 | print: checkbox /CRYBABY/Bypass 0 0 0 1 1 | ||
print: hslider /CRYBABY/Wah-parameter 0.692913 0.8 0 1 0.01 | print: hslider /CRYBABY/Wah-parameter 0.692913 0.8 0 1 0.01 | ||
| + | |||
| + | The second element of the list is the path that should be used to control a specific parameter. The following element is the current value of that parameter, then its default value, minimum value and maximum value. | ||
[[Image:stompbox_faust2pd_patch.png|700px|center]] | [[Image:stompbox_faust2pd_patch.png|700px|center]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | While "~/faust/examples" contains all the "standard" for examples, more Faust codes can be found on the web. In particular, we recommend that you check the [https://ccrma.stanford.edu/~rmichon/faustWorkshops/2016/ 2016 CCRMA Faust Workshop page] that contains a wide range of audio effects. To use them on your Satellite CCRMA, just create a new Faust file using a text editor like leafpad: | ||
| + | |||
| + | leafpad & | ||
| + | |||
| + | and follow the instructions above. Have fun! | ||
Latest revision as of 07:52, 3 July 2016
This tutorial is provided as part of the 2016 CCRMA Stompbox workshop and was written by Romain Michon.
Faust is a functional programming language for real time signal processing. It allows to easily make a wide range of objects going from VST plug-ins to iOS apps for different platforms. This quick tutorial shows how to generate advanced audio effects for PureData using Faust.
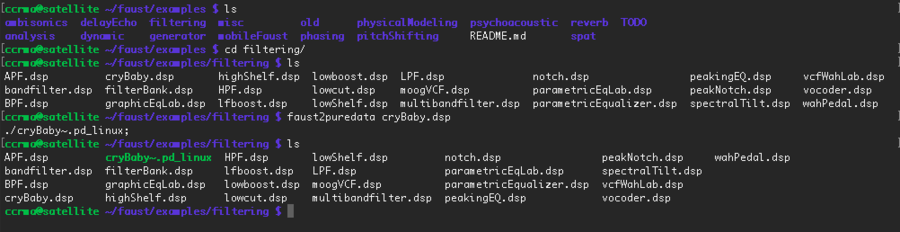
As usual (and as described in here), connect to your Satellite CCRMA using the terminal. If you run the "ls" command, you'll see a list of the folders contained in /home/ccrma. One of these folders is called "faust", go in it by typing "cd faust". If you run "ls" once again, you'll see that this folder contains an "examples" folder. Go in this folder and run "ls". Each of the folder you see contains a series of example Faust codes that can be easily turned into a PD external simply by running the "faust2puredata" command. For example, go in "filtering" ("cd filtering"), run "ls" to see what this folder contains and then run:
faust2puredata cryBaby.dsp
If you run "ls" again you'll see that a file named "cryBaby~.pd_linux" was created. This is a PD external that can be used in any PD patch as long as it is placed in the same folder as the patch that's using it or if it is located in a folder tracked by PD.
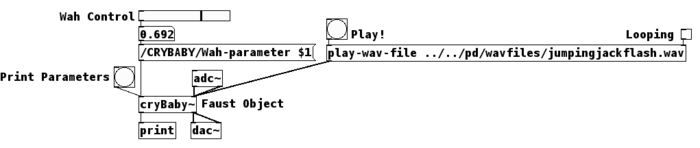
"~/faust/demo/cryBaby.pd" demonstrates how to use a Faust generated PD external. The first inlet takes messages that can be used to control the different parameters of the object. All the other inlets are audio inputs. Similarly, the first outlet can be used to retrieve messages and other outlets are audio outputs. To get a list of the parameters of the object, a bang can be sent to the first inlet and the list will be sent to the first outlet. For example, when a bang is sent to "cryBaby~" (from cryBaby.dsp), the following list is returned:
print: checkbox /CRYBABY/Bypass 0 0 0 1 1 print: hslider /CRYBABY/Wah-parameter 0.692913 0.8 0 1 0.01
The second element of the list is the path that should be used to control a specific parameter. The following element is the current value of that parameter, then its default value, minimum value and maximum value.
While "~/faust/examples" contains all the "standard" for examples, more Faust codes can be found on the web. In particular, we recommend that you check the 2016 CCRMA Faust Workshop page that contains a wide range of audio effects. To use them on your Satellite CCRMA, just create a new Faust file using a text editor like leafpad:
leafpad &
and follow the instructions above. Have fun!