Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
For an ideal mass 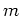 , we have the driving point impedance
, we have the driving point impedance
which, when used to terminate a waveguide of impedance 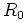 , gives
the reflectance
(continuous time, Laplace domain).
Setting
, gives
the reflectance
(continuous time, Laplace domain).
Setting 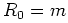 gives
Digitizing using the bilinear transform gives the digital reflectance
The corresponding difference equation is then
simply
(wave digital mass).
gives
Digitizing using the bilinear transform gives the digital reflectance
The corresponding difference equation is then
simply
(wave digital mass).
Next |
Prev |
Up |
Top
|
JOS Index |
JOS Pubs |
JOS Home |
Search
Download SMAC03S.pdf
Download SMAC03S_2up.pdf
![]() , we have the driving point impedance
, we have the driving point impedance